


Next: Antialiasing Filter for Migration
Up: Filtering of coherent noise
Previous: Gulf of Mexico Field
Contents
I have shown that RTM is equivalent to GDM, where the
generalized migration image at a point 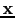 is obtained by taking the dot-product of the GDM
operator with the data. GDM is a generalization
of simple diffraction-stack migration which
sums the data over the hyperbola-like curve associated with the primary reflections.
The advantage of GDM over RTM is that moveout-based
noise can be precisely filtered
from the migration kernel, which can lead to precise
suppression of migration artifacts and avoids unintentional filtering
of data.
In contrast, the standard RTM approach can only
filter the backpropagated data, which is
an inseparable mixture of contributions from both the migration kernel
and data.
I demonstrated the effective reduction of migration noise by
dip filtering the decomposed
migration kernel for both realistic synthetic data and field data.
Some other useful applications of filtered GDM
include mitigation of migration
artifacts due to aliasing and multiples (Zhou et al., 2003; Zhou, 2004).
is obtained by taking the dot-product of the GDM
operator with the data. GDM is a generalization
of simple diffraction-stack migration which
sums the data over the hyperbola-like curve associated with the primary reflections.
The advantage of GDM over RTM is that moveout-based
noise can be precisely filtered
from the migration kernel, which can lead to precise
suppression of migration artifacts and avoids unintentional filtering
of data.
In contrast, the standard RTM approach can only
filter the backpropagated data, which is
an inseparable mixture of contributions from both the migration kernel
and data.
I demonstrated the effective reduction of migration noise by
dip filtering the decomposed
migration kernel for both realistic synthetic data and field data.
Some other useful applications of filtered GDM
include mitigation of migration
artifacts due to aliasing and multiples (Zhou et al., 2003; Zhou, 2004).
The biggest challenge in implementing GDM is the demanding memory and computation
expense of the migration operators. Thus, full blown
GDM should be restricted for now
to smaller data sets, but with wavelet compression
it can be practical for
target-oriented migration and iterative least-squares GDM.



Next: Antialiasing Filter for Migration
Up: Filtering of coherent noise
Previous: Gulf of Mexico Field
Contents
Ge Zhan
2013-07-08