



Next: Shot-domain RTM
Up: Numerical results
Previous: Sensitivity to Velocity Error
Contents
The proposed methods are tested on a 2D marine dataset. There are 515 shots with a shot interval of 37.5 m, and each shot is recorded by a 6 km long cable with 480 receivers and a 12.5 m interval. The nearest offset is 198 m. These 515 CSGs are transformed into common midpoint profiles (CMPs), and 2D spline interpolation is used to fill in the near-offset trace gap after normal moveout. The interpolated data are then transformed into common receiver gathers with a split-spread acquisition geometry using reciprocity (Vigh and Starr, 2008).
In the CRG domain, each trace is multiplied by
 in the frequency domain and then scaled by
in the frequency domain and then scaled by 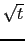 in the time domain to correct for 3D geometrical spreading (Zhou et al., 1995). A tau-p transform is applied to each CRG to generate 31 plane-wave gathers with ray parameters (
in the time domain to correct for 3D geometrical spreading (Zhou et al., 1995). A tau-p transform is applied to each CRG to generate 31 plane-wave gathers with ray parameters ( ) ranging from -333
) ranging from -333 s/m to 333
s/m to 333  s/m with an even sampling in
s/m with an even sampling in  . The plane-wave gathers are filtered with a Wiener filter to transform the original wavelet to a Ricker wavelet with a 25 Hz peak frequency. The original wavelet is estimated by stacking traces with a strong water bottom reflection, and windowing the water-bottom reflection event. Figure
. The plane-wave gathers are filtered with a Wiener filter to transform the original wavelet to a Ricker wavelet with a 25 Hz peak frequency. The original wavelet is estimated by stacking traces with a strong water bottom reflection, and windowing the water-bottom reflection event. Figure ![[*]](file:~/utilities/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) shows the plane-wave gather with a surface shooting angle of zero (
shows the plane-wave gather with a surface shooting angle of zero ( ).
The migration velocity is obtained by waveform inversion (Boonyasiriwat et al., 2010).
).
The migration velocity is obtained by waveform inversion (Boonyasiriwat et al., 2010).
Figure:
A plane-wave gather with zero surface shooting angle (p=0  s/m).
s/m).
|
|




Next: Shot-domain RTM
Up: Numerical results
Previous: Sensitivity to Velocity Error
Contents
Wei Dai
2013-07-10
![\includegraphics[width=5.0in]{./chap3.plane.img/plane.eps}](img170.png)