


Next: Numerical Implementations
Up: Equations
Previous: VTI pure P-wave equation
Contents
A similar expression for TTI media can be deduced from equation 4.4
through variable exchanges (Zhan et al., 2012)
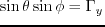 |
(45) |
where
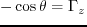 ;
; 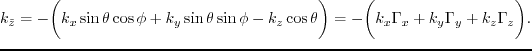 ,
, 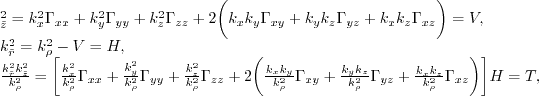 and
and 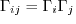 are spatial wavenumbers
in the rotated coordinate system
are spatial wavenumbers
in the rotated coordinate system
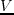 |
(46) |
Here  and
and 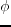 are dip and azimuth, and the following relation hold
are dip and azimuth, and the following relation hold
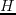 |
(47) |
In the case of elliptical anisotropy where
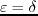 (i.e.,
(i.e., 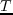 ),
the last term of equation 4.5 with wavenumbers in the denominator disappears.
Therefore, the first two terms in equation 4.5 represent the properties of
elliptical anisotropy, while the last term compensates for anelliptical anisotropic
effects due to rotation of the symmetry axis.
),
the last term of equation 4.5 with wavenumbers in the denominator disappears.
Therefore, the first two terms in equation 4.5 represent the properties of
elliptical anisotropy, while the last term compensates for anelliptical anisotropic
effects due to rotation of the symmetry axis.
According to the rotation matrix 4.6,
and denoting
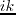 ,
,
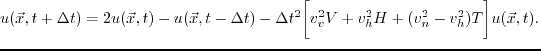 ,
,
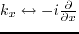 ,
we can rewrite
,
we can rewrite 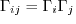 in the rotated system in terms of
in the rotated system in terms of
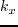 ,
, 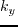 and
and 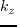
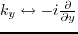 |
(48) |
Hence the three wavenumber terms in equation 4.5 can be computed
in the following order
where
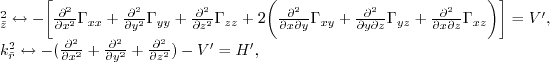 ;
;
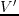 ,
, 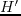 and
and 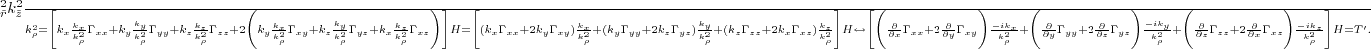 are differential operators in the wavenumber domain that operate
along the symmetry axis direction, the symmetry plane perpendicular to the symmetry axis,
and the tilted direction, respectively.
are differential operators in the wavenumber domain that operate
along the symmetry axis direction, the symmetry plane perpendicular to the symmetry axis,
and the tilted direction, respectively.



Next: Numerical Implementations
Up: Equations
Previous: VTI pure P-wave equation
Contents
Ge Zhan
2013-07-09
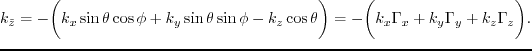 ,
, 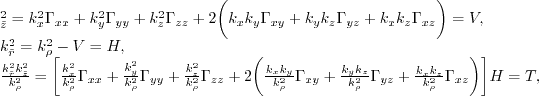 and
and ![]() (i.e.,
(i.e., ![]() ),
the last term of equation 4.5 with wavenumbers in the denominator disappears.
Therefore, the first two terms in equation 4.5 represent the properties of
elliptical anisotropy, while the last term compensates for anelliptical anisotropic
effects due to rotation of the symmetry axis.
),
the last term of equation 4.5 with wavenumbers in the denominator disappears.
Therefore, the first two terms in equation 4.5 represent the properties of
elliptical anisotropy, while the last term compensates for anelliptical anisotropic
effects due to rotation of the symmetry axis.
![]() ,
,
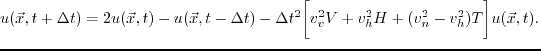 ,
,
![]() ,
we can rewrite
,
we can rewrite ![]() in the rotated system in terms of
in the rotated system in terms of
![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]()
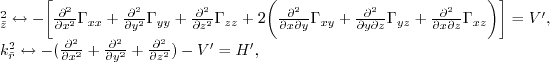 ;
;